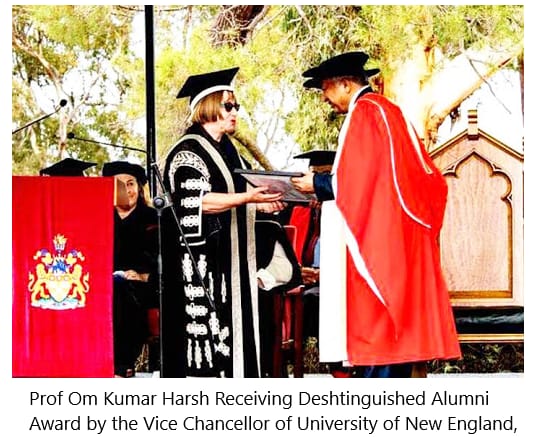
विनय एक्सप्रेस समाचार, ऑस्ट्रेलिया/बीकानेर। बीकानेर मूल के सुप्रसिद्ध प्रो. ओम कुमार हर्ष द्वारा द यूनिक काॅन्सेप्ट ऑफ फिजिक्स सीरीज के चौथे चरण में द्विभाषी संस्करण (हिन्दी एवं अंग्रेजी भाषा) में जारी कर दिया गया है। फिजिक्स क्षेत्र में रूचि रखने वाले विद्यार्थीयों एवं शिक्षकों के लिए प्रो. हर्ष द्वारा प्रदान की गयी जानकारीयां उपयोगी साबित हो रही है।
Vinay Express News, Australia / Bikaner. Famous Prof. of Bikaner origin. The fourth concept of The Unique Concept of Physics Series has been released in the bilingual version (Hindi and English language) by Om Kumar Harsh. For students and teachers interested in Physics field, The information provided by Prof. Harsha is proving very useful.

Before Lecture 4 we want to say something:
Please note that our objective is not provide answers of all questions while our real objective is to prove clearance of concept of some facts of basic physics. We will try our best to give you all conceptual facts related to those physical quantities whose fundamentals are not easily available.
As I asked you the basic facts of the Moment of Inertia of the rigid body during last two chapters, I am happy to tell you that I have already put two videos on this problem one in Hindi and one in English. Please see the YouTube.
कृपया ध्यान दें कि हमारा उद्देश्य सभी प्रश्नों के उत्तर प्रदान नहीं कर रहा है, जबकि हमारा वास्तविक उद्देश्य बुनियादी भौतिकी के कुछ तथ्यों की अवधारणा को साबित करना है। हम उन भौतिक राशियों से संबंधित सभी वैचारिक तथ्यों को देने के लिए अपनी पूरी कोशिश करेंगे, जिनके मूल तत्व आसानी से उपलब्ध नहीं हैं।
जैसा कि मैंने आपसे पिछले दो अध्यायों के दौरान कठोर शरीर के जडत्व आघूर्ण के बुनियादी तथ्यों को पूछा है, मुझे आपको यह बताते हुए खुशी हो रही है कि मैंने इस समस्या पर दो वीडियो पहले ही हिंदी में और एक अंग्रेजी में डाला है। कृपया YouTube देखें।

Lecture: 4
Question 1: Why an object has the potential energy?
Answer: Potential energy of an object is due to its position or orientation on the earth. Because of earth gravitational force every object is associated (or stored in it) with energy without that it cannot occupy any position on the earth.
व्याख्यान: 4
प्रश्न 1: किसी वस्तु में स्थितिजऊर्जा क्यों होती है?
उत्तर: किसी वस्तु की स्थितिजऊर्जा पृथ्वी पर उसकी स्थिति या अभिविन्यास के कारण होती है। पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल के कारण हर वस्तु ऊर्जा के साथ जुड़ी हुई है (या उसमें संग्रहीत है) इसके बिना वह पृथ्वी पर किसी भी स्थिति पर कब्जा/ स्थिर नहीं कर सकती है।
Question 2: Why potential energy is negative at the surface of the earth?
Answer: It is a kind of energy which is required by an object to sustain itself against the earth gravitational force it means some energy is to be supplied ( or work is to be done) on an object in order to make it stand against this force or to bring it at the surface of the earth from a point (infinity) where earth’s gravitational attraction on it zero and therefore it is a negative energy in nature.
There is other reason also that the gravitational energy between earth and the object is the attractive and therefore, because of attraction object will allow to come on the surface of the earth by an external force on it. Negative implies a shortfall, and in this case, it is an energy shortfall. However, positive, or negative energy concept is a relative one and it is the frame or a scale against it is measured.
प्रश्न 2: पृथ्वी की सतह पर स्थितिजऊर्जा नकारात्मक क्यों है?
उत्तर: यह एक प्रकार की ऊर्जा है जिसे किसी वस्तु द्वारा पृथ्वी गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल के विरुद्ध बनाए रखने के लिए आवश्यक है इसका अर्थ है कि इस बल के विरुद्ध खड़े होने के लिए किसी वस्तु पर कुछ ऊर्जा की आपूर्ति की जानी है (या काम किया जाना है)। या इसे एक बिंदु (अनंत) से पृथ्वी की सतह पर लाना जहां पृथ्वी का गुरुत्वाकर्षण आकर्षण शून्य है और इसलिए यह प्रकृति में एक नकारात्मक ऊर्जा है।
अन्य कारण यह भी है कि पृथ्वी और वस्तु के बीच गुरुत्वाकर्षण ऊर्जा आकर्षक है और इसलिए, क्योंकि आकर्षण वस्तु पृथ्वी की सतह पर एक बाहरी बल द्वारा आने की अनुमति देगा। नकारात्मक का अर्थ है एक कमी, और इस मामले में यह एक ऊर्जा की कमी है। हालांकि, सकारात्मक या नकारात्मक ऊर्जा अवधारणा एक सापेक्ष है और यह फ्रेम या इसके खिलाफ एक पैमाने मापा जाता है।
Question 3: What is the kinetic energy and why a body possess it?
Answer: Kinetic energy is a kind of energy that an object or a particle possess it due to its motion. Off course it is a kind of energy, so it is associated with work and therefore with a force also.
A body possess it because a force is required (or released or done by it) to move from one place to place because of earth’s gravitational field.
When we push an object, it acquires a velocity which increases its kinetic energy.If an object falls then it acquires this energy because of earth’s gravitational field.
प्रश्न 3: गतिज ऊर्जा क्या है और क्यों कोई वस्तु इस ऊर्जा को बनाए रखती है
उत्तर: काइनेटिक ऊर्जा एक प्रकार की ऊर्जा होती है जो किसी वस्तु या किसी कण की गति के कारण होती है। बेशक यह एक प्रकार की ऊर्जा है, इसलिए यह काम (work) से जुड़ी है और इसलिए एक बल के साथ भी।
एक वस्तु के पास इसलिए है क्योंकि पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण क्षेत्र के कारण एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान पर जाने के लिए एक बल की आवश्यकता होती है (या इसके द्वारा जारी या किया जाता है)।
जब हम किसी वस्तु को धक्का देते हैं, तो यह एक वेग प्राप्त करता है जो इसकी गतिज ऊर्जा को बढ़ाता है।यदि कोई वस्तु गिरती है तो यह पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण क्षेत्र के कारण इस ऊर्जा को प्राप्त करती है।
Question 4: What is the formula for the kinetic energy and how it comes up?
Kinetic energy formula is ½ mv2 where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity. This formula originates from the following concept:
Let a body of mass m, move with the same velocity u.
Let us move it by distance d, due to continuous force F, working on it.
Work performed on the body of mass ‘m’ is:
W=F× d ……………………………………(i)
As a result of the force F, velocity shifts or changes to u and the acceleration created is ‘f’. Connection between v, u, f and d can be given by equation of motion:
formula v2−u2=2ad
Therefore d=(v2−u2)/2(ii)
F=mf…………(iii)
Substituting (ii) and (iii) in (i) we get
W=F×d
=mf×(v2−u2)/2
W=m(v2−u2)/2
If u=0,(means body is starting from rest)
W= (mv2 ) / 2
Work done=Change in kinetic energy
Therefore Ek=(mv2 ) / 2

प्रश्न 4: गतिज ऊर्जा का सूत्र क्या है और यह कैसे आती है?
गतिज ऊर्जा सूत्र ½ mv2है जहाँ m वस्तु का द्रव्यमान है और v इसका वेग है। यह सूत्र निम्नलिखित अवधारणा से उत्पन्न होता है:
द्रव्यमान m का एक वस्तु, uउसी वेग से चलते हैं।the same velocity u
निरंतर बल F के कारण, इस पर कार्य करते हुए, हम इसे d की दूरी पर ले जाते हैं।
द्रव्यमान ‘m’ के वस्तु पर किया गया कार्य है:
W = F × d ……………………………………… (i)
बल F के परिणामस्वरूप, वेग शिफ्ट हो जाता है या u में बदल जाता है और निर्मित त्वरण ‘f’ है। V, u, f और d के बीच संबंध गति के समीकरण द्वारा दिए जा सकते हैं:
सूत्र v2−u2=2ad
इसलिए d=(v2−u2)/2(ii)
F=mf…………(iii)
Substituting (ii) and (iii) in (i) we get
W=F×d
=mf×(v2−u2)/2
W=m(v2−u2)/2
If u=0,(means body is starting from rest)
अगर u = 0, (मतलब आराम से शुरू हो रहा है)
W= (mv2 ) / 2
काम किया = गतिज ऊर्जा में परिवर्तन
इसलिए Ek = (mv2) / 2
Question 5: What is the relation between Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy:
Answer: When a body is displaced from positions of rest or equilibrium, they acquire energy that was already deposited in the body before being knocked out of rest (equilibrium) by gravity. The potential energy stored in the body is accountable for the energy that arises upon release which is called kinetic energy. Please remember this is only true with macroscopic objects not for atomic or molecular dimensions.
Thus, we see that when we push a body or an object, we impart an energy which is the against the gravity force of the Earth thus by pushing we are working against the position of the body and hence the against the earth gravitational force and this force is converting into the Kinetic Energy of the object. Similarly, if we try to stop a moving object its kinetic energy decrease and the potential energy increases. Thus, it seems that sum of the Potential and Kinetic Energy remains same, yes, it is.
In other words:
The basic connection between the two is their capability to convert into each other. In other words, potential energy converts into kinetic energy, and kinetic energy transforms into potential energy, and then reverse over again.

प्रश्न 5: स्थितिजऊर्जा और काइनेटिक ऊर्जा के बीच क्या संबंध है:
उत्तर: जब एक वस्तुको आराम या संतुलन की स्थिति से विस्थापित किया जाता है, तो वे ऊर्जा प्राप्त करते हैं जो गुरुत्वाकर्षण द्वारा आराम (संतुलन) से बाहर खटखटाए जाने से पहले ही शरीर में जमा हो गई थी। शरीर में जमा होने वाली स्थितिजऊर्जा उस ऊर्जा के लिए जवाबदेह होती है जो रिलीज होने पर उत्पन्होती है जिसे गतिज ऊर्जा कहा जाता है।
इस प्रकार, हम देखते हैं कि जब हम किसी पिंड या वस्तु को धक्का देते हैं, तो हम एक ऊर्जा प्रदान करते हैं, जो पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल के विरुद्ध होती है, इस प्रकार हम धक्का देकर वस्तुकी स्थिति के विरुद्ध काम कर रहे होते हैं और इसलिए पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल के विरुद्ध और यह बल वस्तु के काइनेटिक ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित हो रहा है। इसी तरह, यदि हम किसी गतिमान वस्तु को रोकने की कोशिश करते हैं तो उसकी गतिज ऊर्जा घट जाती है और स्थितिजऊर्जा बढ़ जाती है। इस प्रकार, ऐसा लगता है कि स्थितिजऔर काइनेटिक ऊर्जा का योग समान रहता है, हाँ, यह है।
दूसरे शब्दों में:
दोनों के बीच मूल संबंध एक-दूसरे में बदलने की उनकी क्षमता है। दूसरे शब्दों में, स्थितिजऊर्जा गतिज ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित हो जाती है, और गतिज ऊर्जा स्थितिजऊर्जा में बदल जाती है, और इसका उल्टा भी सच है
Question 6: What are the examples of the Kinetic Energy in the daily life?
Answer: What are kinetic energy examples?
Examples of Kinetic Energy in Everyday Life
- Hydropower Plants. Hydropower plants are places where the generation of electricity takes place with the help of water. …
- Windmills form one of the good examples of applications of kinetic energy. …
- Moving Car. …
- Bullet from a Gun. …
- Flying Airplane. …
- Walking & Running. …
- …
प्रश्न 6: दैनिक जीवन में काइनेटिक ऊर्जा के उदाहरण क्या हैं?
उत्तर: गतिज ऊर्जा उदाहरण क्या हैं?
दैनिक जीवनमें काइनेटिक एनर्जी के उदाहरण
- हाइड्रोपावर प्लांट्स। हाइड्रोपावर प्लांट ऐसे स्थान हैं जहां बिजली का उत्पादन पानी की मदद से होता है। …
- पवनचक्कियां। पवनचक्कियां गतिज ऊर्जा के अनुप्रयोगों के अच्छे उदाहरणों में से एक बनाती हैं। …
- चलती कार। …
- एक बंदूक से गोली। …
- फ्लाइंग एयरप्लेन। …
- चलना और दौड़ना। …
- साइकिल चलाना। …
Question 7: What is the work? How mathematically it can be defined?
Answer: Work as the transfer of energy from one object to another.
Since work = Force . Distance
If someone is involved in pushing and one object pushing another object then our efforts or force is converted into the work which another object (which is being pushed) carries it or stores this work.
Overall, one can say that converting potential energy into the kinetic energy and vice versa are under the force of gravity therefore virtually force of gravity is transformed under this conversation because the objects are under the gravity when they are on the Earth.
प्रश्न 7: कार्यक्या है? गणितीय रूप से इसे कैसे परिभाषित किया जा सकता है?
उत्तर: ऊर्जा का एक वस्तु से दूसरी वस्तु में स्थानांतरण के रूप में कार्य करना।
चूंकि कार्य= बल. दूरी
यदि एक वस्तु को किसी अन्य वस्तु को धकेलता हूं तो हमारा प्रयास या बल उस कार्य में परिवर्तित हो जाता है जिसे कोई अन्य वस्तु (जिसे धकेला जा रहा है) उसे वहन करती है या इस कार्य को संग्रहीत करती है।
कुल मिलाकर, कोई यह कह सकता है कि स्थितिजऊर्जा को गतिज ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित करना और इसके विपरीत गुरुत्वाकर्षण के बल के अधीन हैं इसलिए गुरुत्वाकर्षण के बल को इस बातचीत के तहत रूपांतरित किया जाता है क्योंकि वस्तुएं गुरुत्वाकर्षण के नीचे होती हैं जब वे पृथ्वी पर होते हैं।
Question 8:What is Gravitational Force? What is the Universal law of Gravitation?
Answer: Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation is utilized to describe gravitational force. This law says that every single massive particle in the space attracts every single other massive particle with a force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses andalso inversely proportional to the square of the gap or distance between them.
Newton’s law of universal gravitation
F = (G m1 m2 )/ r2
F = Force , G= Gravitational Constant, m1is the mass of object 1
And m2 is the mass of object 2 and r = is the distance between centres of the masses of m1 and m2
Question 8:Why Newton’s law of universal gravitationexists?
Answer: The answer is property of earth as gravity: an invincible force that drags objects toward each other.
Universal law of Gravitation states that:
F = (GM1M2) /R2
F = Force, G = Gravitational Constant, M1 Mass of object one
M2mass of object 2 और R = distance between centres of M1andM2
प्रश्न 8: गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल क्या है और गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल का न्यूटन नियम क्या है?
उत्तर: गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल का वर्णन करने के लिए न्यूटन के सार्वभौमिक गुरुत्वाकर्षण नियम का उपयोग किया जाता है। यह नियम कहता है कि अंतरिक्ष में हर एक विशाल कण हर एक बड़े पैमाने पर कण को एक बल के साथ आकर्षित करता है जो सीधे उनके द्रव्यमान के उत्पाद के आनुपातिक है और उनके बीच के अंतर या दूरी के वर्ग के व्युत्क्रमानुपाती भी है।
न्यूटन का सार्वभौमिक गुरुत्वाकर्षण का नियम
F = (GM1M2) /R2
F = बल, G = गुरुत्वाकर्षण निरंतर, M1वस्तु 1 का द्रव्यमान है
और M2 वस्तु 2 का द्रव्यमान है और R = M1 और M2 के द्रव्यमान के केंद्रों के बीच की दूरी है
Question 9: why the law of gravitation exists?
Answer: It is the property of the Earth in the form of gravity: an unstoppable force that pulls objects towards each other.
Gravitation is a natural trend by which all things with mass or energy—including planets, stars, galaxies—are bring in toward one another. On Earth, gravity provides weight to physical bodies, and the Moon’s gravity triggers the sea tides.

प्रश्न 9: न्यूटन का सार्वभौमिक गुरुत्वाकर्षण का नियम क्यों मौजूद है?
उत्तर: यह गुरुत्वाकर्षण के रूप में पृथ्वी की संपत्ति है: एक अजेय बल जो वस्तुओं को एक दूसरे की ओर खींचता है।
गुरुत्वाकर्षण एक प्राकृतिक प्रवृत्ति है जिसके द्वारा द्रव्यमान या ऊर्जा के साथ सभी चीजें-जिनमें ग्रह, तारे, आकाशगंगा शामिल हैं-एक दूसरे की ओर लाते हैं। पृथ्वी पर, गुरुत्वाकर्षण भौतिक निकायों को वजन प्रदान करता है, और चंद्रमा का गुरुत्वाकर्षण समुद्री ज्वार को ट्रिगर करता है।
Question 10: What is the acceleration due to gravity?
Definition:
Anybodysituated in the field of the earth suffers a gravitational drag. Gravitational acceleration is defined as the bodycatching an acceleration as a result of force of gravity working on it in the earth’s gravitational field. It is characterized by ‘g’ and its unit is m/s2. Gravitational acceleration is a quantity of vector, that is it has together magnitude and direction.
प्रश्न 10: गुरुत्वाकर्षण के कारण त्वरण क्या है?
परिभाषा:
पृथ्वी के क्षेत्र में स्थित कोई भी व्यक्ति गुरुत्वाकर्षण खींचता है। गुरुत्वाकर्षण त्वरण को पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण क्षेत्र में इस पर काम करने वाले गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल के परिणामस्वरूप त्वरण को पकड़ने वाले वस्तु के रूप में परिभाषित किया गया है। इसकी प्रतीक’g’ है और इसकी इकाई m / s2है। गुरुत्वाकर्षण त्वरण वेक्टर की एक मात्रा है, अर्थात इसमें परिमाण और दिशा एक साथ है।
Question 11: What is the formula for the acceleration due to gravity?
Formula:
Applying the following equation, the gravitational acceleration working on anybody can be explained as
g=GM/(r+h)2
Here, G is the universal gravitational constant (G = 6.673×10-11 N.m2/Kg2.)
M is the mass of the body whose gravitational force performs on the given body under the given situation.
r is the planet radius.
h is the height of the body from the body surface.
When the body is on or near the surface of the earth, the force of gravity working on the body is nearly constant and the subsequent equation can be utilized.
g=GM/r2

प्रश्न 11: गुरुत्वाकर्षण के कारण त्वरण का सूत्र क्या है?
सूत्र:
निम्नलिखित समीकरण को लागू करना, गुरुत्वाकर्षण त्वरण
g=GM/(r+h)2
यहाँ, G सार्वभौमिक गुरुत्वाकर्षण स्थिरांक है (G = 6.673 × 10-11 N.m2 / Kg2)।
mवस्तु का द्रव्यमान है जिसका गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल स्थिति के तहत दिए गए वस्तु पर प्रदर्शन करता है।
r ग्रह त्रिज्या है।
h शरीर की सतह से वस्तु की ऊंचाई है।
जब वस्तु धरतीकी सतह पर या उसके पास होता है, तो वस्तु पर काम करने वाले गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल लगभग स्थिर होते हैं और निम्नलिखितसमीकरण का उपयोग किया जा सकता है:g=GM/r2
Question 12:What are factors does g (Acceleration due to gravity) depends on?
“g” implies to acceleration due to gravity.
Factors on which g varies are:
Height b. Depth c. Shape of earth d. Rotation of earth.
Height : “g” reduces as one goes away from the surface of the Earth.
it is controlled by formula , g’= g [ 1 – (2h/R) ] , where h is the height , R is radius therefore when g’=0, height h = R ,.
Depth : The value of gravitational acceleration reduces if one goesnear the center of the Earth. It is controlled by formula g’=g [ 1-(d/R)]where d is depth, R is radius
Shape : As earth is not aideal sphere , it radius alongsideequator is greater than that of poles. That is: Re >Rp
Now as we know g = GM/R2 that is g varies inversely on square of radius therefore
“g”at poles is larger than that of value g at equator.
Therefore, value of g reduces when we go from poles to equator.
Rotation of the Earth:
Here we are not giving its explanation because it is for higher classes.
प्रश्न 12: गुरुत्वाकर्षण के कारण त्वरण किस कारक पर निर्भर करता है?
“g” गुरुत्वाकर्षण त्वरण जिन कारकों पर जी भिन्न होता है:
ऊँचाई b गहराई c पृथ्वी का आकार d पृथ्वी का घूमना।
ऊँचाई: “g” पृथ्वी की सतह से दूर जाने के कारण कम हो जाता है।
यह सूत्र द्वारा नियंत्रित किया जाता है, g ‘= g [1 – (2h / R)], जहाँ h ऊँचाई है, R त्रिज्या है इसलिए ऊँचाई h = R, g’ = 0।
b.गहराई: गुरुत्वाकर्षण त्वरण का मान कम हो जाता है अगर कोई पृथ्वी के केंद्र के पास जाता है। यह सूत्र g ‘= g [1- (d / R)] द्वारा नियंत्रित किया जाता है जहां d की गहराई है, R त्रिज्या है
c.आकार: जैसा कि पृथ्वी एक आदर्श क्षेत्र नहीं है, यह भूमध्य रेखा के साथ त्रिज्या ध्रुवों की तुलना में अधिक है। वह है: Re> Rp
अब जैसा कि हम जानते हैं कि g = GM/R2है जो कि इसलिए g त्रिज्या के वर्ग पर विपरीत रूप से भिन्न होता है
ध्रुवों पर “g” भूमध्य रेखा पर मान g से बड़ा है।
इसलिए, जब हम ध्रुवों से भूमध्य रेखा पर जाते हैं, तो जी का मूल्य कम हो जाता है।
d.पृथ्वी का घूमना:
यहां हम इसकी व्याख्या नहीं दे रहे हैं क्योंकि यह उच्च वर्गों के लिए है।
जानिये क्या है यूनिक काॅन्सेप्ट ऑफ फिजिक्स सीरीज: विश्व विख्यात प्रोफेसर डाॅ. ओके हर्ष ने जारी किया मिशन एंड विजन
सुप्रसिद्ध प्रो. हर्ष एवं एन.एल.सेवग द्वारा संचालित यूनिक काॅन्सेप्ट ऑफ फिजिक्स के दुसरे चरण की प्रश्नोत्तर जारीः यहां क्लिक कर पढे़ं पूरा आलेख
द यूनिक काॅनसेप्ट ऑफ फिजिक्स श्रृंखला के तीसरे चरण का आलेख जारी
द यूनिक काॅनसेप्ट ऑफ फिजिक्स श्रृंखला के तीसरे चरण का आलेख जारी
द यूनिक काॅन्सेप्ट ऑफ फिजिक्स के वाॅट्सएप ग्रुप से जुड़ने के लिए यहाँ क्लिक करें।
द यूनिक काॅन्सेप्ट ऑफ फिजिक्स के टेलीग्राम ग्रुप से जुड़ने के लिए यहाँ क्लिक करें।
द यूनिक काॅन्सेप्ट ऑफ फिजिक्स के फेसबुक पेज से जुड़ने के लिए यहाँ क्लिक करें।
विनय एक्सप्रेस के यूट्यूब चैनल के माध्यम से देख सकेगें प्रो. हर्ष के विडियोज
प्रो. ओम कुमार हर्ष द्वारा विनय एक्सप्रेस के यूट्यूब चैनल पर द यूनिक काॅन्सेप्ट आॅफ फिजिक्स सीरीज का विडियो वर्जन के माध्यम से फिजिक्स प्रेमियों के लिए फिजिक्स के यूनिक काॅन्सेप्ट समझाने का प्रयास किया जा रहा है।
प्रो. हर्ष के विडियोज देखने के लिए निम्नांकित लिंक पर क्लिक करें
पहला विडियो
दूसरा विडियो
अंग्रेजी वर्जन विडियो